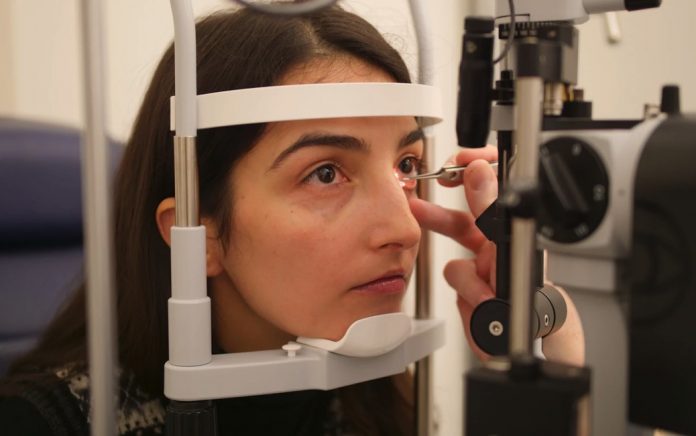
หญิงชาวโปรตุเกสที่ถูกจัดว่าเป็นผู้พิการทางสายตาในทางกฎหมายกลับมามีสายตาดีขึ้นกว่า 20/20 หลังจากเป็นผู้แรกในสหราชอาณาจักรที่ได้รับการผ่าตัดเลเซอร์ใหม่ซึ่งใช้ AI ในการช่วยประมวลผล
แพทริเซีย กอนซัลเวส วัย 31 ปีจากโปรตุเกส เป็นผู้ป่วยรายแรกในสหราชอาณาจักรที่ได้รับการผ่าตัด Lasik แบบใหม่ที่คลินิกเอกชนในกรุงลอนดอนเมื่อสัปดาห์นี้
กอนซัลเวส ซึ่งเพิ่งจบการศึกษาระดับปริญญาโทจากมหาวิทยาลัยออกซ์ฟอร์ด มีปัญหาสายตาเอียงและสั้นขั้นรุนแรง ซึ่งถือว่าตาบอดในทางกฎหมายเมื่อไม่มีแว่นตาช่วย
กระบวนการผ่าตัดนี้เริ่มจากการสแกนดวงตาและสร้างแบบจำลองดิจิทัลของดวงตาของเธอขึ้นมา จากนั้นโปรแกรม AI จะทดลองกับแบบจำลองนี้เพื่อออกแบบการรักษาที่เฉพาะเจาะจงสำหรับปัญหาสายตาของกอนซัลเวส ก่อนที่ศัลยแพทย์จะดำเนินการรักษาบนดวงตาจริงของเธอ
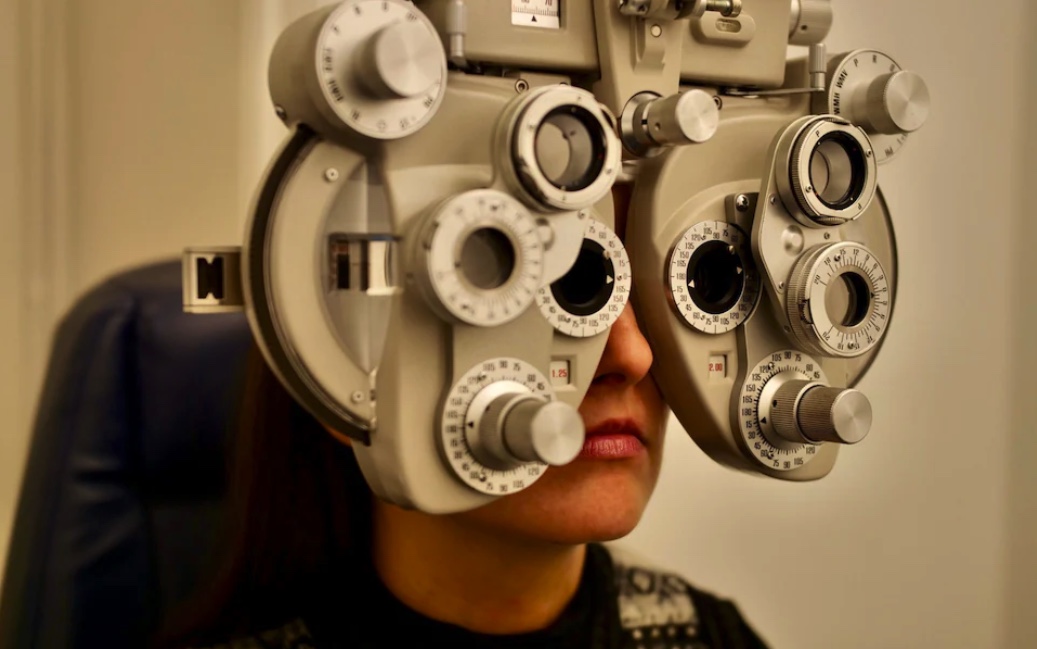
การผ่าตัดในราคา 6,500 ปอนด์ที่ Focus Clinics กรุงลอนดอน โดยนายแพทย์ David Allamby ประสบความสำเร็จ ทำให้เธอมีสายตาที่ชัดถึงระดับ 20/16 ซึ่งดีกว่าระดับ 20/20 ที่เป็นมาตรฐานสำหรับค่าสายตาที่ดี และบ่งบอกถึงความสามารถในการมองเห็นที่ชัดเจนในระยะ 20 ฟุต
“เธอสวมแว่นตามาตั้งแต่อายุ 5 ขวบ และหากไม่มีแว่นก็แทบจะมองไม่เห็นตัวอักษร ‘E’ ขนาดใหญ่บนแผ่นตรวจสายตา” นายแพทย์ Allamby กล่าวกับ The Telegraph
“ก่อนผ่าตัด สายตาของเธอแย่กว่าระดับ 20/200 และเมื่อใส่แว่นแล้วก็มองเห็นได้เพียงระดับ 20/20 วันนี้เธอสามารถมองเห็นได้ในระดับ 20/16 ซึ่งดีกว่า 20/20 และสามารถอ่านตัวอักษรในบรรทัดถัดไปในแผ่นตรวจสายตาได้”
เทคโนโลยีจำลองดวงตาดิจิทัลที่ชื่อว่า “Eyevatar” ใช้เวลาประมาณ 10 นาทีในการสแกนดวงตาและรวบรวมข้อมูล ก่อนที่คอมพิวเตอร์จะจำลองลำแสงเลเซอร์ 2,000 ชนิดเพื่อหาวิธีที่มีผลดีที่สุดต่อการมองเห็น
เทคโนโลยีนี้เคยถูกใช้ในประเทศจีนและออสเตรเลียมาก่อน และตอนนี้มีให้บริการในสหราชอาณาจักรแล้ว
“เนื่องจากฉันมีปัญหาสายตาเอียง ฉันไม่เคยสามารถใส่คอนแทคเลนส์ได้อย่างสบาย และการมองเห็นในตอนกลางคืนก็ไม่ดีเท่าไหร่ ฉันรู้สึกตื่นเต้นที่จะได้ลองการผ่าตัดดวงตาด้วยการเรย์เทรซิงและหวังว่าจะได้สัมผัสผลลัพธ์ด้วยตัวเอง” กอนซัลเวส กล่าวก่อนเข้ารับการผ่าตัด
ข้อมูลจากการทดลองทางคลินิกของเทคโนโลยีนี้ในผู้ป่วย 200 รายที่เผยแพร่เมื่อปีที่แล้ว ระบุว่าทุกคนมีสายตาที่ดีกว่าระดับ 20/20 หลังการผ่าตัดไปแล้วสามเดือน
หนึ่งใน 12 การผ่าตัดมีผลให้ผู้ป่วยมีสายตาระดับ 20/10 ซึ่งนายแพทย์ Allamby ระบุว่า “เป็นขีดจำกัดสูงสุดสำหรับดวงตามนุษย์” และดีเท่ากับ 2 เท่าของระดับ 20/20
กระบวนการนี้ยังทำงานเพื่อลดการกระจายภาพ (Point Spread Function หรือ PSF) ซึ่งเป็นการบิดเบือนของภาพบนเรตินาให้ใกล้เคียงกับภาพที่เห็นจริงมากที่สุด
Blind woman has better than 20/20 vision after AI surgery
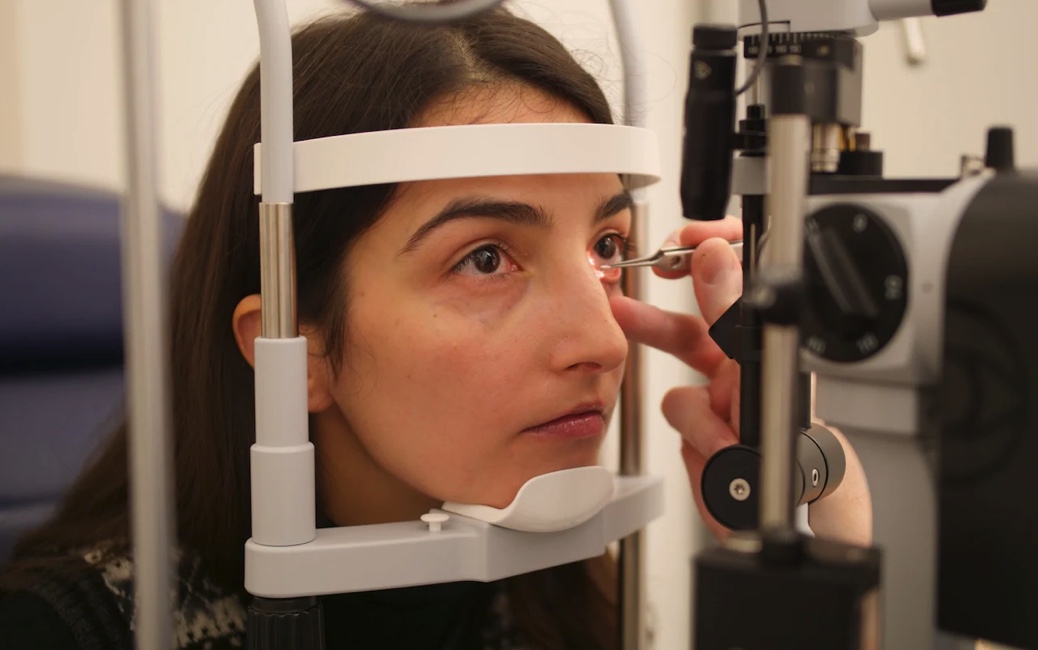
A legally blind woman now has better than 20/20 vision after becoming the first person in the UK to undergo a new type of AI-powered laser surgery.
Patrícia Gonçalves, 31, from Portugal, was the first patient in the UK to undergo the new Lasik surgery, at a private clinic in London this week.
Ms Gonçalves, who has just completed a master’s degree at the University of Oxford, was legally blind without glasses because of astigmatism and extreme short-sightedness.
The procedure involved scanning her eyes and creating a digital clone of her eyeballs. An artificial intelligence program then experimented on the digital replica to create a bespoke procedure to treat Ms Gonçalves’ failing eyesight. A surgeon then performed the treatment on her.

Her £6,500 procedure on Thursday at Focus Clinics in London by chief eye surgeon Mr David Allamby was a success and she now has 20/16 vision, which is better than 20/20.
20/20 is the benchmark for eyesight and is considered to be a normal visual acuity, which is the ability to see clearly at a distance of 20ft.
“She has worn glasses since five years old, is legally blind without glasses and cannot see the huge ‘E’ letter at the top of the eye test chart,” Mr Allamby told The Telegraph.
“Her best vision pre-op was worse than 20/200 and with glasses was just 20/20. Today, she can see 20/16, so better than 20/20, and has gained one more line down the test chart.”
The “Eyevatar” digital clone technology takes around 10 minutes to scan the eye and gather the data before a computer mimics around 2,000 different laser beams to see what will have the best impact on vision.
It has been used in China and Australia before and is now available in the UK.
“Having astigmatism, I’ve never been able to wear contact lenses comfortably, and my night vision isn’t great. I’m excited to get ray-tracing eye surgery and look forward to experiencing the results first hand,” Ms Gonçalves said ahead of her procedure.
Data from a clinical trial of the technology on 200 people published last year disclosed that every single eye had better than 20/20 vision three months after the surgery.
One in 12 procedures resulted in 20/10 vision, which Mr Allamby says is “the absolute limit for a human eye” and twice as good as 20/20.
The procedure works to minimise what opticians know as the point spread function (PSF), which is the extent to which an image is distorted on the retina compared with reality.
By Joe Pinkstone, The Telegraph